What is Google Ads Manager? How does it work and what are the differences between Google Ad Manager and other advertising platforms? Let’s find out with Bigfouth LTD in the following article.
Introduction to What Is Google Ad Manager

Google Ad Manager (GAM) is a comprehensive ad server and management platform designed by Google to help publishers manage their entire digital ad inventory across devices and formats.
With GAM, publishers can:
- Manage ad campaigns and line items
- Sell ad space directly or programmatically
- Control creatives and placements
- Leverage advanced targeting options
- Access detailed performance reporting
It is the next step up from Google’s AdSense, with more sophisticated features and higher revenue potential.
Some key advantages of Google Ad Manager include:
| Feature | Benefit |
| Unified auction | Increased demand and yield |
| Granular targeting | Higher CPMs |
| Programmatic deals | Flexible monetization |
By centralizing ad operations, GAM makes it easier for publishers to optimize ad revenue and growth. This guide provides an overview of its core capabilities.
Key Features of Google Ad Manager
Google Ad Manager is packed with features to help publishers manage ad inventory, create and deliver campaigns, and generate actionable reports.
Inventory Management
The inventory tab is where publishers can configure their available ad spaces or ad units. You can set up different sizes, formats, and targeting capabilities for each individual unit.
Other inventory components include:
- Mobile apps – Manage in-app ad spaces
- Key-values – Create custom targeting parameters
- Targeting presets – Save and reuse targeting configurations
With robust inventory organization, it’s easier to sell your ad spaces and maximize revenue.
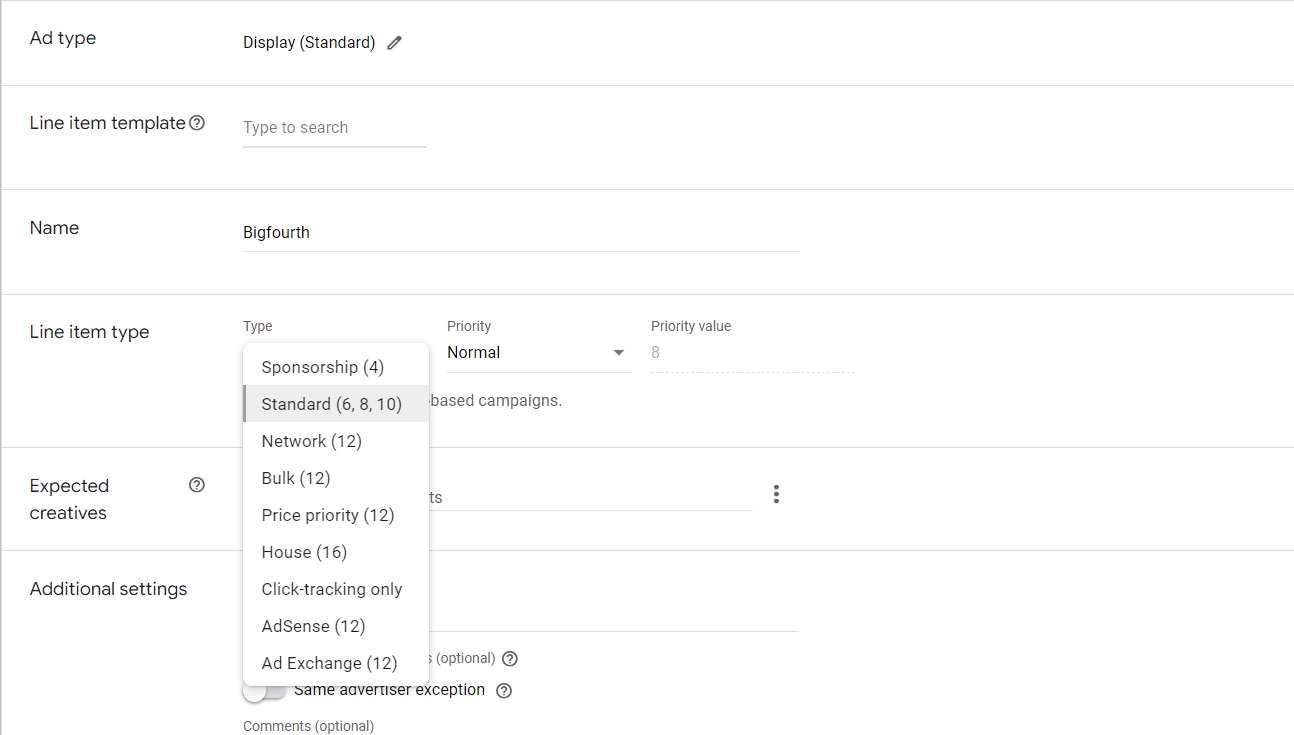
Line Items
Line items contain the core details for each ad campaign, including:
- Budget or impression goals
- Start and end dates
- Targeting criteria
- Ad creative specs
- Billing method
Line items belong to orders, which represent advertisers. You can assign different priority levels to each line item to control the ad serving sequence.
Creatives
The creatives tab lets you upload and manage the actual ads or creatives. You can traffic image files, videos, HTML5 creatives, or just input the ad tag.
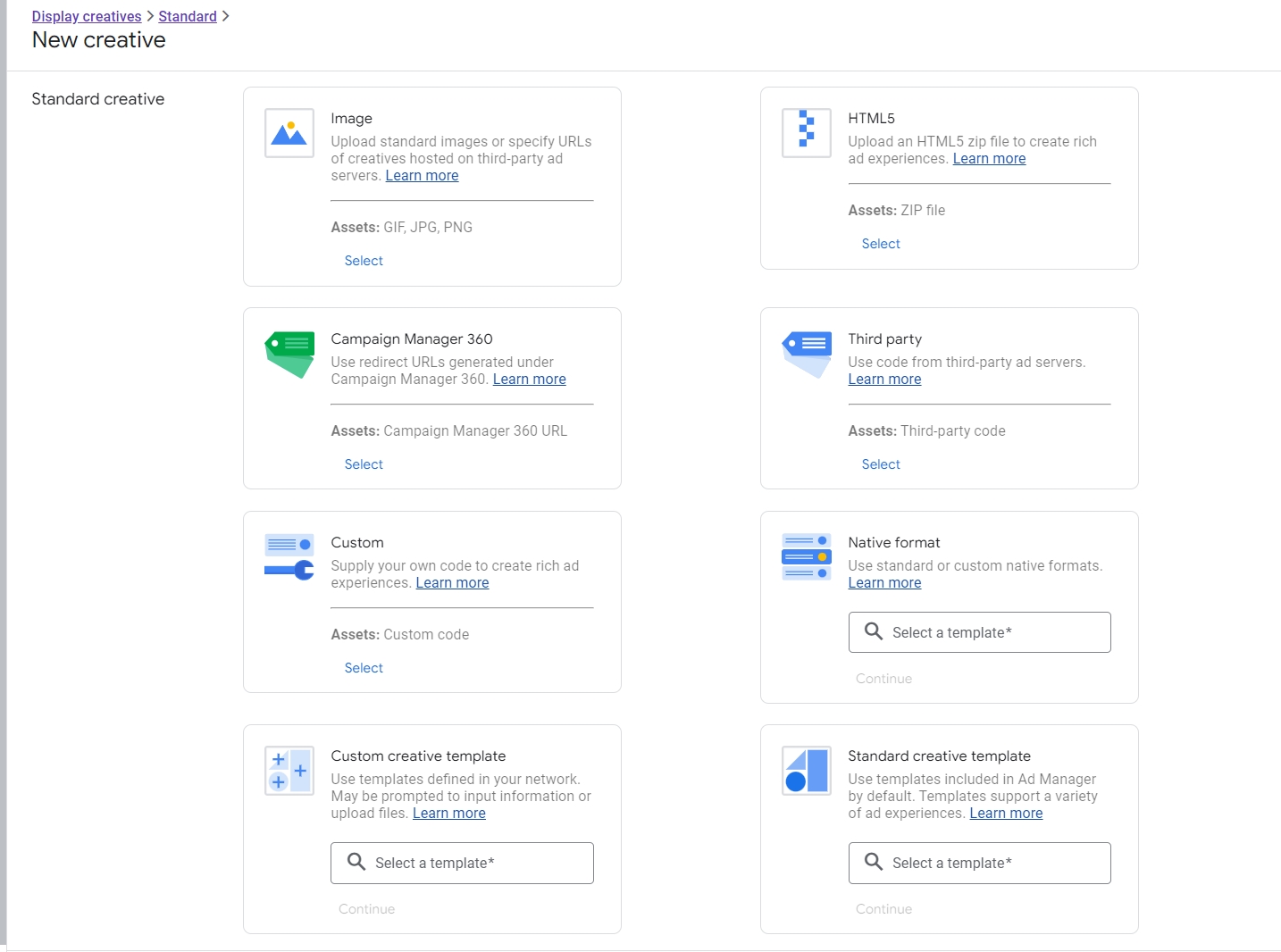
GAM will store and serve each creative according to the specifications set in the associated line item.
Targeting Options
What Is Google Ad Manager enables advanced targeting through a variety of options:
- Key-values – Custom parameters for matching ads to inventory
- Geography – Country, region, city, etc.
- Devices – Desktop, mobile, tablet, etc.
- Browsers – Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.
- Frequency capping – Limit impressions per user
Layering different targeting methods allows you to create laser-focused segments and increase the value of your ad spaces.
Reporting
GAM provides a powerful reporting interface to analyze performance data. You can:
- Build custom reports with multiple dimensions and metrics
- Export results to Excel, CSV, etc.
- Schedule and email reports
- Use templates for quick reporting
Segmenting data by line item, order, creative, placement, or other dimensions gives you visibility into what’s working and what’s not.
Additional Capabilities
Other notable GAM features include:
- Automated ad trafficking and delivery
- Forecasting inventory availability
- Direct integrations with AdSense and Ad Exchange
- Programmatic demand channel
- Native ad support
- Robust admin tools and user permissions
With its comprehensive capabilities, Google Ad Manager provides publishers with an all-in-one platform to optimize ad monetization.
How Google Ad Manager Works
Now that we’ve covered the key capabilities, let’s look at how What Is Google Ad Manager actually functions under the hood.
Unified Auction
One of the core components is GAM’s unified auction, which brings together demand from multiple sources:
- Google Ad Exchange – Programmatic demand
- AdSense – Google’s ad network
- Open bidding – Approved third-party demand partners
- Header bidding – Client-side wrappers
Rather than running separate auctions, GAM uses a single simultaneous auction to surface the highest bid across all demand sources vying for each impression.
This simplified flow increases competition, drives up pricing, and boosts publisher yield.
Programmatic Deals
In addition to real-time auctions, What Is Google Ad Manager supports programmatic deals between advertisers and publishers:
- Private marketplace – Private, invite-only auctions
- Preferred deals – Fixed CPM or percentage of impressions reserved for specific buyers
- Programmatic guaranteed – Automated direct deals
- Line items can be configured to target different types of deals to balance guaranteed demand with real-time auctions.
Integration with Adsense and Ad Exchange
As Google’s ad platform, GAM is deeply integrated with both AdSense and Ad Exchange:
- Easily add an AdSense line item to compete for impressions
- Leverage additional demand from Ad Exchange auctions
- Manage both through a single interface and set of reports
AdSense effectively serves as a revenue floor while Ad Exchange provides opportunity for greater earnings.
Auction and Delivery Workflow
When a user visits a page with GAM ad tags, the following happens:
- Ad tags call GAM for bid requests
- GAM runs unified auction across demand sources
- Winning bids are notified and creatives cached
- Creatives are returned and displayed to user
- Impression data is recorded for reporting
This simplified workflow illustrates how Google Ad Manager leverages technology to optimize ad selection and delivery for publishers.
By providing robust tools and maximizing yield, GAM empowers publishers to effectively monetize their ad inventory across channels and buyers.
Advanced Features
In addition to core ad management capabilities, What Is Google Ad Manager offers several advanced features to further enhance monetization.
Open Bidding
Open bidding, formerly known as exchange bidding, allows publishers to open up their inventory to demand from outside networks beyond just Google’s.
Once enabled, approved third-party demand partners can bid directly on impressions in real-time. This increases competition and drives up pricing.
Some benefits of open bidding include:
- Access demand beyond Google’s ecosystem
- Preserve user experience (vs header bidding)
- Control which demand partners participate
With open bidding, publishers can tap into a broader pool of advertisers.
Header Bidding
What Is Google Ad Manager also supports header bidding through a unified setup.
Rather than managing separate wrapper codes, you can enable client-side header bidding demand directly through GAM.
- Define partner-specific timeouts
- Set minimum bids for each partner
- Monitor performance in GAM reports
This hybrid header bidding approach helps maximize publisher yield.
Testing and Optimization
GAM provides a dedicated testing environment for trying new configurations before deploying them:
- Test ad unit setups and creatives
- Experiment with different line item strategies
- Refine targeting parameters
- Confirm desired configurations
Thoroughly testing before launching helps identify the optimal setups for maximizing revenue.
Additional Advanced Tools
- Forecasting – Predict available impressions and revenue
- Protections – Block undesirable ads
- Troubleshooting – Diagnose delivery issues
- Admin – Manage users, permissions, settings
- Dynamic allocation – Automated rule-based allocation
- Native ads – Customizable in-feed ad units
- Mobile app integration – Monetize in-app inventory
With its robust feature set, What Is Google Ad Manager provides publishers with the capabilities needed to optimize ad revenue across devices, ad formats, and demand channels.
Benefits of Using Google Ad Manager

Google Ad Manager offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive choice for publishers looking to maximize ad revenue.
Increased Revenue
By centralizing ad management and enabling competition between demand sources, GAM helps publishers increase earnings from their ad inventory. Key revenue drivers include:
- Unified auction – Surfaces the highest bids across all demand channels
- Programmatic deals – Support for higher CPM direct deals and private auctions
- AdX and AdSense – Additional demand layers from Google’s networks
- Open and header bidding – Access to more advertisers and increased competition
According to Google, adoption of Unified Auction yielded an average revenue lift of 8-15% for publishers.
Granular Targeting
GAM provides sophisticated targeting capabilities to create highly segmented ad inventory packages.
- Key-values – Custom definitions for ad targeting
- Presets – Easily save and reuse targeting configurations
- Audience targeting – Target user interests and demographics
- Contextual – Target pages or sections based on content
With more granular targeting, publishers can better align inventory with advertiser demand and charge higher rates.
Detailed Reporting
Robust reporting and analytics help publishers optimize ad performance:
- Break down results by dimensions like ad unit, placement, geography
- Filter data by date ranges, line items, creatives, and more
- Surface actionable insights into revenue metrics
- Identify high-performing areas of inventory
- Diagnose issues impeding revenue
With data-driven decision making, publishers can fine-tune strategies to improve monetization.
Other Benefits
- Simplified workflow – Manage all ad operations from a single platform
- Time savings – Automate previously manual processes like campaign trafficking
- Security – Reduce risk and control which ads are displayed
- Support – Get access to Google’s technical support resources
- Ease of use – User-friendly UI with robust features
- Industry standards – Integrates policies like ads.txt for fraud prevention
With its unique combination of sophisticated capabilities, revenue maximization tools, and publisher security features, What Is Google Ad Manager, it provides compelling benefits for publishers.
Getting Started with Google Ad Manager
Ready to start using Google Ad Manager? Here is an overview of what’s involved in the setup and launch process:
Sign Up Requirements
To create a GAM account, you need:
- A Google account
- Ownership of the site domain
- Google AdSense account
For Ad Manager 360, you’ll need to work directly with a Google sales rep.
Interface Walkthrough
The GAM interface consists of these core sections:
- Inventory – Configure ad units and targetting
- Delivery – Create line items and upload creatives
- Reporting – Build and analyze reports
- Admin – Manage users, settings, etc.
Take time to understand how each section works and how they fit together.
Inventory Setup
- Create a variety of ad unit sizes and formats.
- Enable video ad capabilities as needed.
- Set up key-values for custom targeting.
- Organize inventory into packages and placements.
Properly structured inventory makes selling ads simpler.
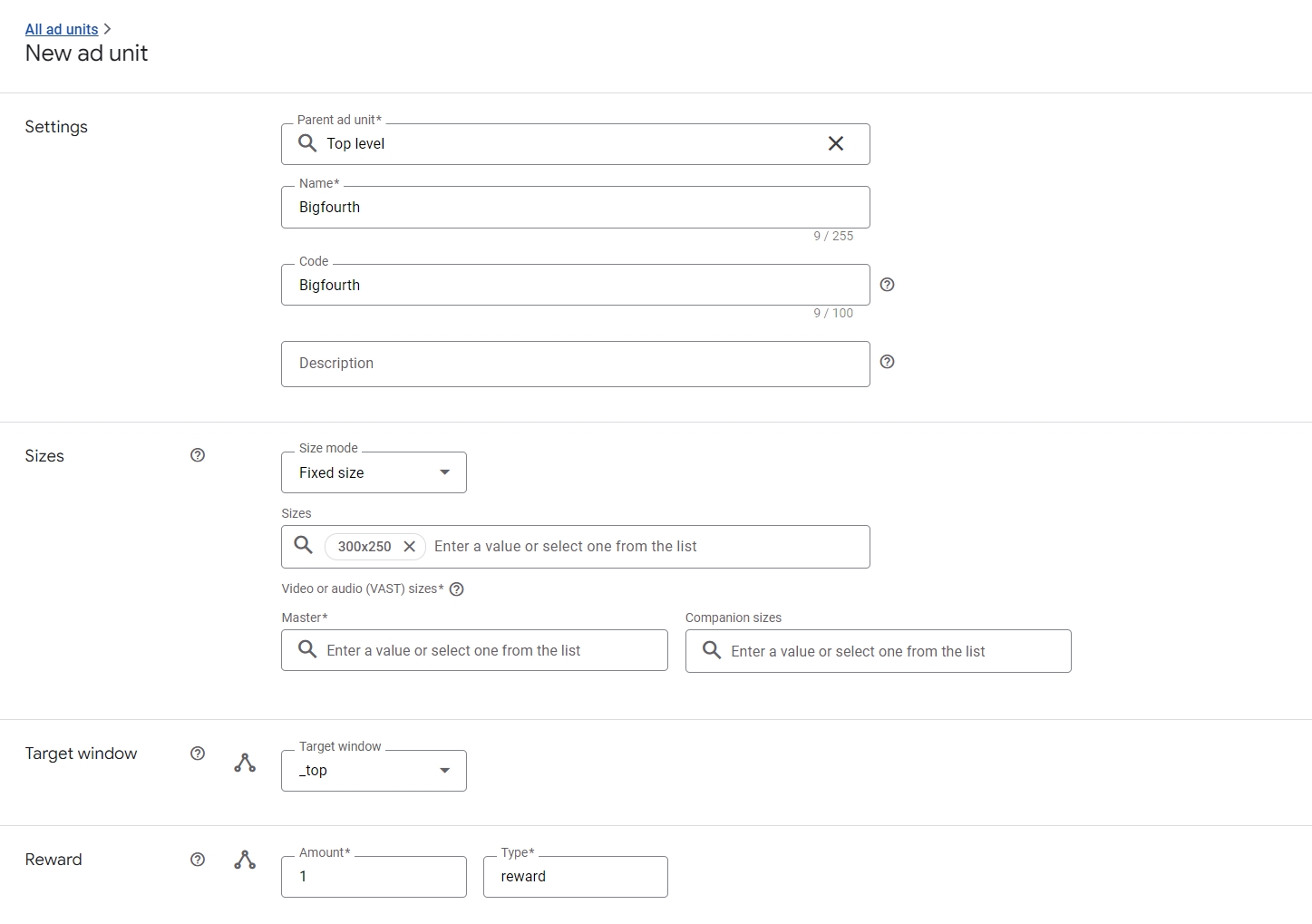
Creating Campaigns
- Build out orders for each advertiser or buyer.
- Configure line items based on the deal specifics like ad types, budgets, targeting, etc.
- Upload creatives or input third-party ad tags.
- Set up reporting labels for tracking.
Methodical campaign configuration helps maximize returns.
Tag Implementation
- Generate ad tags for each GAM ad unit.
- Place tags on sites and apps through direct code insertion, Google Tag Manager, or ad server wrappers.
- Confirm tags are loading correctly.
- Perform comprehensive ad unit testing.
Proper tag implementation ensures ads deliver as expected.
Launch and Optimization
- Activate campaigns and start serving live ads.
- Review reporting dashboards and metrics regularly.
- Optimize line item targets, creatives, bidding, and targeting based on performance.
- Build additional demand channels through open bidding, header bidding etc.
Continuous optimization maximizes ad revenue over time.
With these steps complete, you’ll have fully configured Google Ad Manager to monetize your ad inventory. Be sure to regularly assess new features and capabilities as GAM continues rapidly evolving.
Google Ad Manager Vs Other Google Products
Google offers several ad products. How does Ad Manager compare to options like AdSense and Google Ads?
Difference from AdSense

Google AdSense is a network that serves contextual text and display ads on websites. Publishers paste a code snippet to show ads targeted by Google based on page content.
Pros
- Easy setup and management
- Little maintenance required
- Access to Google’s advertiser base
Cons
- Limited control over ad types
- Lower earnings compared to direct-sold ads
- Less reporting and optimization capabilities
AdSense works best for new publishers or blogs with lower traffic. For more established publishers, Ad Manager provides greater control, customization, and monetization capabilities.
GAM also allows publishers to keep using AdSense demand as one channel along with other direct and programmatic deals.
Comparison to Google Ads
Google Ads (formerly AdWords) enables advertisers to show ads across Google’s network, including search results and partner sites via services like AdSense.
Ads allows advertisers to:
- Create text, display, and video ad campaigns
- Target users based on keywords and demographics
- Set daily budgets and bids for keywords
Ads focuses on the advertiser side. Ad Manager is tailored for publishers to better monetize inventory.
Key differences:
| Google Ads | Google Ad Manager |
| Advertiser-facing | Publisher-facing |
| Buy ad placements | Sell ad placements |
| Broad reach across web | Manage owned inventory |
| Pay for clicks/conversions | Get paid for impressions |
So in summary, Google Ads helps brands buy ad space on Google and partner sites. Ad Manager helps publishers sell their direct inventory more effectively.
When to Use Each
- Publishers should use Google Ad Manager to maximize earnings from their sites and apps.
- Advertisers should use Google Ads to reach customers across the web through paid search and display advertising.
- AdSense works best for new publishers lacking resources to directly sell ads.
Selecting the right Google advertising platform depends on your goals and role in the digital ad ecosystem.
Best Practices for Using Google Ad Manager
To get the most out of Google Ad Manager, be sure to follow these best practices:
Inventory Organization
- Create a logical ad unit structure based on site content and layout.
- Set up strategic placements to help buyers navigate your inventory.
- Use descriptive key-values for custom targeting.
- Group similar sites/apps to streamline management.
Smart inventory organization makes selling ads more efficient.
Custom Reporting
Leverage reporting to uncover optimization opportunities:
- Analyze dimensions like geography, browser, device type, ad unit etc.
- Add metrics like impressions, clicks, CTR, revenue etc.
- Build reports to diagnose issues and identify high-value sections.
- Schedule reports for weekly or monthly delivery.
Segmented data provides visibility to make informed decisions.
Header Bidding Setup
Properly configure header bidding for maximum returns:
Limit to 2-3 partners to avoid latency issues. Set appropriate partner-specific timeouts. Only use partners likely to beat direct sales. Monitor partner performance in reports.
With the right header bidding approach, increased competition drives higher earnings.
AdX and AdSense Strategy
- Add AdX demand for an additional auction layer.
- Enable AdSense as a supplementary fallback monetization source.
- Manage via a single order and set of line items for each.
- Optimize between direct-sold, AdX, and AdSense.
Layering Google’s networks boosts yield beyond direct sales.
Page-Level Setup
Place ad tags strategically based on content. Keep mobile layouts simple – one ad per page. Use video ads sparingly to avoid interference. Test different ad sizes and formats.
Optimizing placement and format improves viewer response.
Following these tips and best practices will help you maximize revenue from What Is Google Ad Manager. Continually refine your setup and strategy based on performance data.
The Future of Google Ad Manager
What Is Google Ad Manager is constantly evolving with new features and capabilities. What does the future look like for GAM and ad monetization?
Recent Developments
Some notable recent additions include:
- Unified pricing – Simplified pricing rules across networks
- Creative rotation – Automated sequencing of creatives
- Audience sharing – Sync first-party data for better targeting
- Mobile app SDK – Streamlined SDK for in-app monetization
Google is focused on making GAM more robust while simplifying workflows.
Upcoming Features
Google plans further enhancements around identity, privacy, and automation.
Privacy
- Support for privacy frameworks like GDPR and CCPA
- Tools to manage consumer consent
- Limited data usage and enhanced security
Identity
- Alternatives to third-party cookies
- Contextual targeting to reduce reliance on user data
- Publisher first-party audience sharing
Automation
- Bidding algorithms to optimize return
- Workflow automation for operational efficiency
- Increased AI-driven management capabilities
Industry Trends
Some evolving ad industry trends to watch for:
- Rise of connected TV (CTV) and video
- Audio ads for smart speakers and podcasts
- Contextual and interest-based targeting
- Convergence of linear TV and digital video
- Shoppable ads that drive direct response
Google Ad Manager will likely expand features in these high-growth areas.
Final Thoughts
GAM’s development roadmap will focus on maximizing publisher revenue while providing greater transparency, control, and flexibility.
As digital advertising matures, expect continued consolidation around scaled platforms like Google Ad Manager that provide robust tools to manage complex omnichannel monetization.
Embracing emerging channels, ad formats, and automation technologies will be key to staying competitive. Google is positioning Ad Manager to be the go-to platform for holistic ad management now and in the future.
Conclusion
In summary, What Is Google Ad Manager, it is a powerful ad monetization platform that brings major benefits for publishers.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key points covered in this guide:
- GAM provides robust inventory management, line item configuration, advanced targeting, and actionable reporting.
- The unified auction drives competition across demand channels to increase yield.
- Programmatic deals balance guaranteed revenue with real-time auctions.
- AdX and AdSense integrations boost earnings.
- Features like open bidding and header bidding access more demand.
- Customizable reporting uncovers optimization opportunities.
- Automation and advanced capabilities simplify workflows.
With its comprehensive feature set, Google Ad Manager empowers publishers to effectively monetize ad inventory across devices, formats, and buyers.
Role in Digital Advertising
For publishers, Google Ad Manager has become:
- The premium ad management platform
- The industry standard for monetization
- A certified partner requirement
- A proven path to revenue growth
Ad Manager consolidates ad operations into a single, sophisticated platform to maximize yield.
For advertisers, GAM provides:
- Access to top, brand-safe premium publishers
- Targeted reach across devices and formats
- Advanced automation and targeting
- Transparent pricing and auction dynamics
With benefits on both the buy and sell-side, Google Ad Manager sits at the center of the digital advertising ecosystem.
Bigfourth LTD is a leading google ad manager service provider
As an industry leader in Google AdSense and Google Ad Exchange optimization, Bigfourth LTD provides publishers expert guidance on maximizing revenue with Google’s advertising platforms. This includes leveraging sophisticated tools like What is Google Ad Manager (GAM), the premium ad management platform discussed throughout this guide. With deep expertise optimizing GAM and Google’s ecosystem, bigfourth.com empowers publishers to fully capitalize on these monetization opportunities.
Bigfourth.com’s core services help publishers properly configure and optimize Google Ad Manager to drive higher revenue. Their Google AdSense Optimization manages all aspects of AdSense implementation, from tag setup to reporting. For GAM, they assist with inventory and order configuration, programmatic integration, advanced targeting techniques, and customized reporting. Bigfourth.com also provides Publisher Website Optimization to maximize page RPMs. With Google Ad Exchange services, publishers gain access to premium demand and CPMs.
As covered in this guide, What Is Google Ad Manager unlocks significant monetization potential through capabilities like unified auctions, open bidding, and robust analytics. With deep expertise in these areas, Bigfourth can help publishers fully realize GAM’s revenue benefits. Their technical knowledge, hands-on support, and optimization best practices enable publishers to expertly navigate Ad Manager and other Google offerings.
For publishers seeking to boost earnings through platforms like Google AdSense, Ad Exchange, and Ad Manager, Bigfourth LTD is an ideal partner. Their combination of strategic consulting and technical implementation provides a proven formula for ad revenue growth.
Contact Bigfourth LTD
Website: https://bigfourth.com/
Email: [email protected]
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/bigfourth/
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/bigfourth/
In Closing
This guide provided a comprehensive overview explaining What Is Google Ad Manager, its key features for publishers, and how to get started.
By leveraging Google’s robust monetization tools, publishers can save time, boost revenue, and optimize ad operations.
